Allows Access to Any Piece of Data in the File Without Reading the Data That Comes Before It?
In a calculator, a file arrangement -- sometimes written filesystem -- is the manner in which files are named and where they are placed logically for storage and retrieval. Without a file organisation, stored information wouldn't be isolated into individual files and would exist difficult to identify and retrieve. As data capacities increase, the arrangement and accessibility of private files are becoming even more of import in data storage.
Digital file systems and files are named for and modeled after newspaper-based filing systems using the same logic-based method of storing and retrieving documents.
File systems tin can differ betwixt operating systems (Os), such as Microsoft Windows, macOS and Linux-based systems. Some file systems are designed for specific applications. Major types of file systems include distributed file systems, disk-based file systems and special purpose file systems.
How file systems work
A file system stores and organizes data and can be thought of as a blazon of index for all the data contained in a storage device. These devices can include hard drives, optical drives and flash drives.
File systems specify conventions for naming files, including the maximum number of characters in a name, which characters can be used and, in some systems, how long the file name suffix can be. In many file systems, file names are not example sensitive.
Along with the file itself, file systems contain information such equally the size of the file, as well as its attributes, location and hierarchy in the directory in the metadata. Metadata tin can also identify free blocks of available storage on the drive and how much space is available.
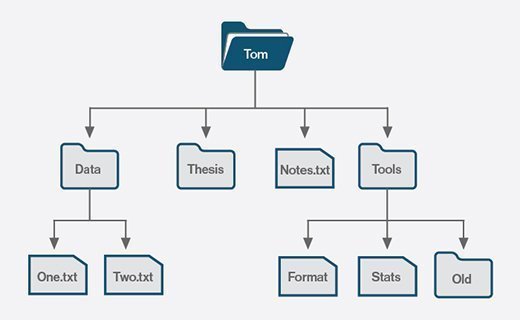
A file system also includes a format to specify the path to a file through the construction of directories. A file is placed in a directory -- or a folder in Windows OS -- or subdirectory at the desired place in the tree structure. PC and mobile OSes have file systems in which files are placed somewhere in a hierarchical tree structure.
Before files and directories are created on the storage medium, partitions should be put into identify. A partition is a region of the hd or other storage that the Bone manages separately. One file system is contained in the main partition, and some OSes let for multiple partitions on 1 disk. In this state of affairs, if one file organisation gets corrupted, the data in a different partition will be prophylactic.
File systems and the office of metadata
File systems use metadata to shop and retrieve files. Examples of metadata tags include:
- Date created
- Engagement modified
- Concluding date of access
- Concluding fill-in
- User ID of the file creator
- Access permissions
- File size
Metadata is stored separately from the contents of the file, with many file systems storing the file names in separate directory entries. Some metadata may be kept in the directory, whereas other metadata may be kept in a structure chosen an inode.
In Unix-similar operating systems, an inode can shop metadata unrelated to the content of the file itself. The inode indexes data past number, which can be used to admission the location of the file and so the file itself.
An example of a file system that capitalizes on metadata is Os Ten, the OS used by Apple tree. It allows for a number of optimization features, including file names that can stretch to 255 characters.
File organisation access
File systems can also restrict read and write access to a item grouping of users. Passwords are the easiest way to exercise this. Forth with controlling who can alter or read files, restricting admission can ensure that data modification is controlled and limited.
File permissions such as access or capability control lists tin also be used to moderate file organisation access. These types of mechanisms are useful to prevent access by regular users, but not equally effective confronting outside intruders.
Encrypting files tin also prevent user access, merely it is focused more on protecting systems from exterior attacks. An encryption key can exist applied to unencrypted text to encrypt it, or the fundamental can be used to decrypt encrypted text. Only users with the cardinal tin admission the file. With encryption, the file organisation does not need to know the encryption fundamental to manage the data finer.
Types of file systems
There are a number of types of file systems, all with dissimilar logical structures and backdrop, such as speed and size. The type of file system tin can differ by Bone and the needs of that Os. The iii most common PC operating systems are Microsoft Windows, Mac Os Ten and Linux. Mobile OSes include Apple tree iOS and Google Android.
Major file systems include the post-obit:
File allocation table ( Fatty ) is supported past the Microsoft Windows Os. Fat is considered uncomplicated and reliable, and it is modeled afterwards legacy file systems. Fatty was designed in 1977 for floppy disks, only was later adjusted for hard disks. While efficient and compatible with nigh current OSes, Fat cannot match the performance and scalability of more modern file systems.
Global file arrangement (GFS) is a file organisation for the Linux OS, and information technology is a shared deejay file system. GFS offers directly access to shared block storage and can be used as a local file system.
GFS2 is an updated version with features non included in the original GFS, such as an updated metadata system. Nether the terms of the GNU General Public License, both the GFS and GFS2 file systems are bachelor as complimentary software.
Hierarchical file system (HFS) was developed for use with Mac operating systems. HFS tin can also be referred to as Mac Bone Standard, and it was succeeded by Mac Os Extended. Originally introduced in 1985 for floppy and difficult disks, HFS replaced the original Macintosh file arrangement. It can also be used on CD-ROMs.
The NT file organisation -- likewise known as the New Technology File System ( NTFS ) -- is the default file arrangement for Windows products from Windows NT 3.1 OS onward. Improvements from the previous Fat file arrangement include improve metadata back up, performance and use of disk space. NTFS is also supported in the Linux OS through a free, open-source NTFS driver. Mac OSes have read-but support for NTFS.
Universal Deejay Format (UDF) is a vendor-neutral file arrangement used on optical media and DVDs. UDF replaces the ISO 9660 file organisation and is the official file system for DVD video and audio as chosen by the DVD Forum.
File system vs. DBMS
Like a file organisation, a database management organization (DBMS) efficiently stores data that can be updated and retrieved. The 2 are non interchangeable, however. While a file system stores unstructured, often unrelated files, a DBMS is used to store and manage structured, related data.
A DBMS creates and defines the restraints for a database. A file organisation allows access to unmarried files at a fourth dimension and addresses each file individually. Because of this, functions such as redundancy are performed on an private level, not by the file system itself. This makes a file system a much less consistent course of data storage than a DBMS, which maintains 1 repository of data that is defined once.
The centralized construction of a DBMS allows for easier file sharing than a file system and prevents anomalies that can occur when separate changes are fabricated to files in a file arrangement.
In that location are methods to protect files in a file system, but for heavy-duty security, a DBMS is the mode to go. Security in a file system is determined by the OS, and information technology tin can be difficult to maintain over time as files are accessed and authority is granted to users.
A DBMS keeps security constraints high, relying on countersign protection, encryption and limited authority. More security does result in more obstacles when retrieving data, and so in terms of general, simple-to-employ file storage and retrieval, a file system may be preferred.
File systems definition evolves
While previously referring to physical, paper files, the term file system was used to refer to digital files equally early on as 1961. By 1964, it had entered general utilize to refer to computerized file systems.
The term file organisation can also refer to the role of an Bone or an add-on program that supports a file system. Examples of such addition file systems include the Network File System (NFS) and the Andrew File Organization (AFS).
In addition, the term has evolved to refer to the hardware used for nonvolatile storage, the software application that controls the hardware and architecture of both hardware and software.
Source: https://www.techtarget.com/searchstorage/definition/file-system
0 Response to "Allows Access to Any Piece of Data in the File Without Reading the Data That Comes Before It?"
Post a Comment